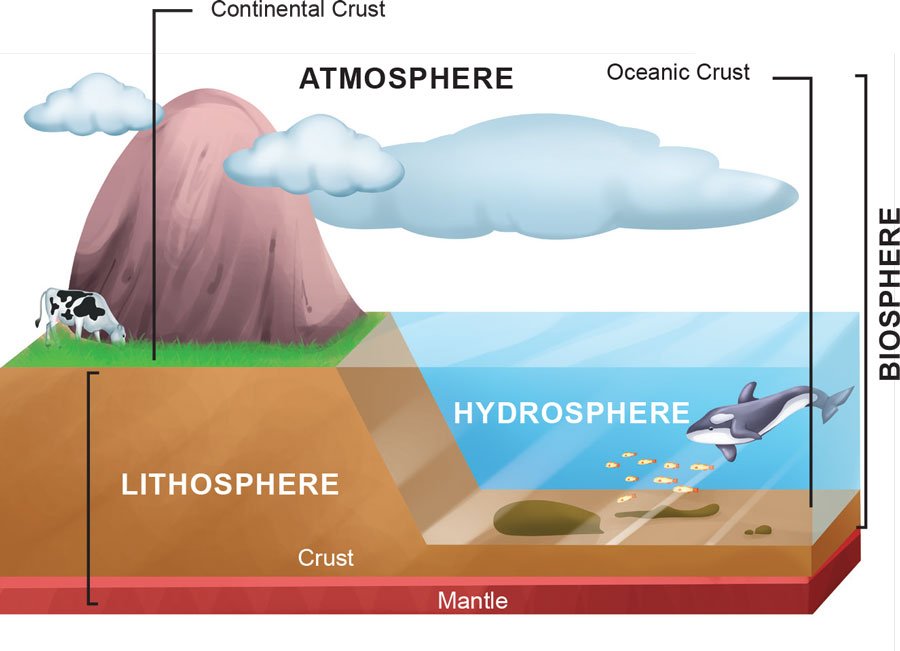
The crust is the outermost part of the Earth and is also called the lithosphere. The crust of the Earth is divided into two parts: continental crust and oceanic crust. The land part or continents are formed by the continental crust. The continental crust is made up of rocks that consist of primarily silica (Si) and aluminia (Al) and hence called ‘sial’. On an average, the thickness of this part of the crust varies from 35 to 70 km. The second part is the ocean crust, which is situated below the oceans. The oceanic crust consists of silica (Si) and magnesium (Mg) and hence called ‘sima’. The ocean crust is thin (5-10 km) and dense in comparison to continental crust.
Lithosphere: Lithosphere is composed of the outer layer of the Earth’s crust and the upper mantle. It is made up of rock slabs called crustal plates (tectonic plates).
Hydrosphere: The parts of the crust that hold water is called hydrosphere. It is comprised of oceans, seas, rivers, lakes and streams.