Land use : India has about 32.88 crore hectares of land. From this total land we have a data of 92.5% land area. This land is used in cultivation, forests, industries etc. The following table explains the land use :
Land use % put to use
1. Cultivated land 51.00
2. Forests 19.03
3. Waste land 14.01
4. Cultivable waste 6.04
5. Fallow land 5.00
6. Pastures and Meadows 4.00
The second largest population in the world and also the largest population of cattle in the world is fed by agriculture in India. It also provides the raw materials to several agro-industries of India. We are left with some land that can be brought under cultivation in future. At the same time, to sustain our cattle population we not to clear our forests and pastures.
Importance of Irrigation in India : A huge quantity of our water resources are used for irrigation of land. 50% of our cultivated area receives marginal rainfall. Due to the uncertainity of rains, such areas face drought conditions once in three or four years. Irrigation ensures at least one crop during a year and enables the cultivation of more than one crop from the same field during a year. Farms which are irrigated produce larger yield per hectare as compared to rainfed areas.
Ways in which Irrigation helps us : We can increase agricultural yield by giving water to the crops, when they need it. Crops in rains deficient areas can be grown. Thus, irrigation can help us in growing crops all the year round, despite scanty rains.
Water Resources and their Utilization in India
Water resources of India are of two types :
(i) Surface Water Resources : India receives an average of 109 cm of rainfall per year. This rainfall amounts to 37,000 million cubic metre. Out of this, 12,500 million cubic metres evaporates due to heat and another 7,900 million cubic metres is absorbed in land. Only 16,600 million cubic metres water is available in our rivers. Out of this, only 6600 million cubic metres water is used for irrigation. During 1996, India could use only 40% of this water for irrigation.
(ii) Underground Water Resources : Out of total rainfall, only 7900 million cubic metres water percolates down the earth. Out of this, about 4300 million cubic metres water is able to reach the upper layer of the soil. This water has a role in agricultural production. Rest 3600 million cubic metres reaches the impervious rocks which can be used by digging wells or tubewells. Out of this, the use of only 2250 million cubic metres water is economically viable.
Facilities for Irrigation in India
In India, irrigation factors are favourable.
(i) Cultivated land in the river basins is flat where canals can be constructed.
(ii) There are many rivers flowing in northern India which make water available throughout the year for irrigation purposes.
(iii) Soils in northern India are move fertile and canals construction is easy.
(iv) In most parts of India, sufficient underground water can be utilized for irrigation by digging wells and tubewells.
(v) Mountainous and rocky terrain in different parts of our country provide excellent sites for the construction of dams useful for irrigation and power production.
(vi) In the southern plateau of India, there are natural hollows in rocky parts.
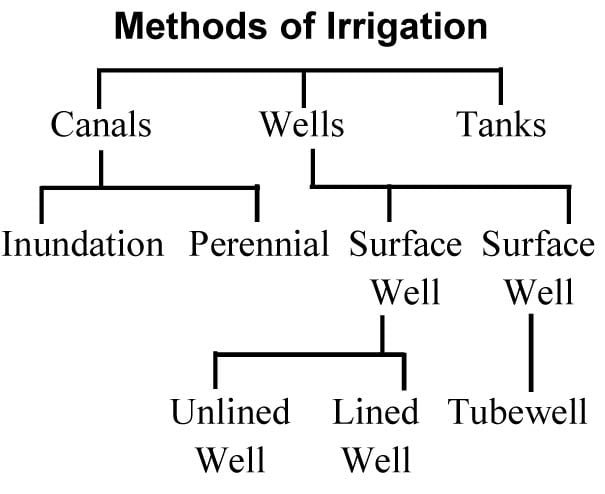
Where lot of rain water goes in to these hollows, which is utilized for irrigation.
Power Resources of India
India uses a large number of renewable sources of energy, viz., hydroelectric power, thermal power, petroleum, atomic power, solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy and bio-gas, etc.
Multipurpose Projects of India
Multipurpose river valley projects provide an integrating system of controlling floods, generation of hydroelectricity, irrigation, development of fishery and tourist spots, boating, navigation, and draining away extra water. These projects aim at allround development of river valleys.


