Abrasion : It is the wearing away of ground by particles of rocks by rivers, ice or the wind. It is a type of land erosion by running water, glaciers, waves and strong winds.
Absolute age : The age of a rock mineral or fossil. It is measured by radiometric method.
Absolute humidity : The amount of water vapour present in a unit volume of air. It is the grams of water per litre of air.
Absolute temperature : A temperature scale based on absolute zero of temperature. In this scale freezing point of water is 273.16K.
Abyssal : It is the sea bed at water depths of greater than 2000 m. Abyssal hill and plain are also popular terms.
Abyssal Hill : Feature of the deep ocean floor ranging from 1000 meter high and a few kilometres wide.
Acid Lava : It is the lava which flows from a volcano before solidifying. These volcanoes are dome shaped with step sloping sides.
Acid rain : It is polluted rain which harms environment, trees and limestone buildings. Limestone buildings weathering takes place more quickly.
Activity : It is the total flow of energy through a system in a unit time.
Actual vegetation : Vegetation that actually exists at the time of observation.
Aerobic : Active only in the presence of oxygen.
Aestivation : Dormancy of certain animals during summer.
Afforestation : This is the process of planting plants and trees in places where they did not grow before.
Aggradation : It is the raising up of land surface by deposition of rock material.
Agric : It is the depositional soil horizon having clay and humus.
Agricultral Revolution (New) : Methods of recent farming in more economically developed countries. In this methods of intensive food production have been used.
Airconditioning : The process of controlling the temperature and humidity is known as airconditioning.
Air Mass : A mass of air extending over a large height of about 1000 km having distinct characterstics of temperature, humidity and lapse rate.
Air Pollution : Air having abnormal constituents of sulphur dioxide, co, oxides of nitrogen, dust and other substances is called air pollution.
Alluvium : The sediments like clays, silts, sand etc. deposited by a river. The flood plains and deltas of large rivers are formed of alluvium.
Alpine : The parts of mountain above tree line but below permanent snow.
Alternative energy : Sources other than the burning of coal, oil and gas. These are mainly wind power, solar power, hydrothermal power, wave and tidal power.
Altitude : It is the height of a place above sea level in metres.
Alternative Technology : Technology that aims to use resources sparingly and to do minimum damage to environment.
Altostratus : A high level layer of cloud over a large part of sky.
Anemometer : It is an instrument used for measuring wind speed.
Angaraland : It is the oldest land mass situated north to Tethys sea.
Animal unit : A unit of livestock equivalent of a mature cow. One cow is considered equivalent to one horse, one mule, five sheep or six goats.
Annotation : The labelling of a map, sketch or diagram is called annotation.
Anticyclone : This is a large but temporary area of high pressure in the atmosphere. They are usually slow moving and last for a number of days over a place.
Aquifer : It is the underground layer of rock which holds large amounts of water.
Arable : This farming is that which focuses on growing crops, cereals and vegetables by ploughing the land.
Arbosist : An arborist is a person who studies tree.
Arch : An arch is a rocky coastal feature, which is found along high coastlines.
Arid : Arid is a place with a very dry climate. Deserts have an arid climate.
Artificial Rain : A rain which is caused by an artificial stimulus such as common salt.
Artesian well : This is a well sunk into an artesian basin. In these basins a layer of permeable rock, is sandwiched between impermeable layers. Water from the edges of the basin gets trapped in this aquifer. The high water pressure in the aquifer causes the well water to gush to the surface like a fountain.
Asteroid : These are the amall celestail bodies revolving round the sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. They are also called minor planets.
Atlas : A book of maps, diagrams and information useful in the study of geography.
Atmosphere : The atmosphere is the layer of gas around the earth. Most of our weather and climate takes place in the lower 7-8 miles (12 km) of the atmosphere where water vapour exists. The atmosphere is heated from below. Radiation from the sun passes through it largely unabsorbed by the air. It is absorbed by the Earth’s surface which warms the atmosphere above it. Atmosphere contains 79% nitrogen, 20% oxygen and rest other gases.
Attrition : This is the wear and tear of particles transported by either rivers, waves or the wind.
Auger : An investment used for drilling and collecting cores of soil deposits.
Auxins : These are plant hormones.
Avalanche : It is the fast moving snow, ice, rock down a slope. Avalanches occur in mountain regions.
Back wash : Back wash is the return flow of a wave back towards the sea.
Balance of nature : Ecological balance is called balance of nature.
Bankful : This occurs when a river’s water level reaches the top of its channel.
Bar : A bar is a ridge of sand and shingle offshore from a coastline.
Bar chart : It is a chart showing vertical colums rising from a horizontal axis. More complicated data can be presented by a bar chart.
Barometer : It is an instrument used for measuring atmospheric pressure.
Barrage : It is an obstruction or dam built across an estuary.
Barrier split : A beach barrier connected to the mainland at our end and terminating in the open water.
Baryte : It is a barium mineral.
Basaltic lava : Lava with the composition of basalt.
Base flow : The part of the discharge of a river/stream. It comes from ground water supplies.
Base level : It is the sea level for most rivers.
Basic lava : It is the molten rock from within the earth which is fluid in state.
Basin : An area drained by rivers.
Bathyal : It applies to sea bed and sediments.
Bay : A bay is a wide and deep indentation along a coast line.
Beach : Deposition of sandy and pebbly materials by waves along a coast line.
Beach barrier : A wide ridge of sand protruding above normal high tide level.
Beaufort scale : It is a numerical scale for recording wind speed.
Bedding plane : This is the line which divides each layer on strata in a sedimentary rock.
Biennial : A plant whose life is two years e.g. carrot.
Biocide : Any agent than is able to kill living organisms.
Biological weathering : Biological weathering occurs when plants and animals are involved in the weathering of rock.
Biomass : The amount of live vegetation in an area is called biomass.
Biosphere : The area where the lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere are in contact with each other and in which life exists is called biosphere.
Birth rate : The number of live births per 1000 people in a year is called birth rate.
Boulder clay : A mixture of stones/boulders and sticky clay is called boulder clay.
Bovine : The cattles which provide milk.
Braiding : Braiding occurs when a river splits from a single river into several channels. These channels are known as distributaries.
Break or Burst : Burst of the monsoon refers to the sudden approach of the moisture laden winds along the coast of Kerala which causes heavy rains.
Bridge point : A bridge point is the place where a bridge has been or could be built across a river. This crossing point of the river develops into an important route centre and meeting place. Sea, river and road travel meet here.
Brown Smoke : Smoke produced by volatile tarry substances emitted by coal.
Calcification : Calcification is the deposition of calcium in a soil profile because of weak leaching.
Calcimorphic soils : These are the soils having excess lime material.
Canopy : It is a high layer of vegetation in a woodland. In equatorial rain forests this layer of tall trees can cut out sunlight for the layers below.
Canyon : A large gorge is called canyon.
Carboniferous limestone : It is a sedimentary rock and one of the types of limestone.
It is a hard rock forming high ground.
It is pervious and permeable.
Cardinal points : The north, south, east and west points including the four directions of a compass.
Cartography : It is the science and skill of making maps and charts.
Cash crops : These are the crops grown for sale rather than for consumption by the farmer and family, such as jute, coconut etc.
Catchment area : It is the supply area for a river or a service such as a school or shopping centre.
Cave : An underground hollow in the ground with an opening onto the earth’s surface.
Census : A census is the data collection about the size and nature of the population done once every ten years.
Chalk : Chalk is a permeable sedimentary rock.
Channel : The trough between two banks in which a stream/river’s water flows. These have banks and a bed.
Charcoal : Impure carbon obtained by burning coal etc.
Chemical weathering : It is defined as the break-up of rocks due to the chemicals in air and water.
Chernozem : It is a grassland soil. It gets developed on continental grasslands.
Chestnut soil : Similar to chernozem soils but found in warmer areas of low rainfall.
Chloropleth : A chloropleth is a map which uses colour-shading, line-shading or stippling to show the distribution of population over the Earth.
Cirques : These are semicircular basins with steep sides and gently sloping floor.
Circle of lllumination : It is the circle which divides the earth into a half lit and a half dark.
City climate : Change in city climate due to fog, humidity, rain etc.
Cliff recession : These are sloping rock surfaces along a coastline.
Climate : The changes in weather from day to day, constitute climate.
Climatic region : It is a large area of the earth in which every part has a broadly similar climate.
Climatography : It is a graph showing the average monthly values for temperature and rainfall at a place.
Climax vegetation : It is a plant community which is ideally suited to its environment.
Clouds : These are masses of minute water droplets and/or ice crystals visible in the sky. Clouds are formed when a large body of air cools to its dewpoint and the water vapour condenses into cloud.
Coastline : The coastline is the stretch of land which borders the sea.
Cold front : It is defined as the boundary between advancing cold air and stationary warm air.
Collective farming : It is an arrangement in which government land is farmed by a group of people who work together sharing resources, production and profits.
Colostrum : The milk produced during the first few days after a mamal has given birth.
Combustion : Burning of fuels to produce heat is called combustion.
Comet : Bodies of solar system that moves around the sun in long elliptical orbits.
Commercial farming : It is the growing of crops or rearing of livestock for sale in the market.
Commune : It is a large unit of land which is owned and managed by the people living on it.
Community : Any naturally occuring group of organisms.
Composite volcano : It is made up of many layers of lava, ash and any other materials ejected from inside the Earth.
Compression : The force by which different parts of the earth’s crust move towards each other.
Condensation : The process by which water vapour are converted into water.
Confluence : The meeting point of two or more river channels.
Coniferous forests : Coniferous evergreen cone bearing trees with needle shaped leaves.
Conservation : It is the process of maintenance and protection of resources.
Conservation of Energy : Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, only its form can be changed.
Constellation : A definite pattern of group of stars in the sky.
Constructive waves : These waves make the material to accumulate on a shore.
Continent : A very big mass of land such as Asia, Africa etc.
Continentality : It is the climate of a place which is not affected by the influence of the sea.
Continental climate : Climate in the interior of the continent which is very hot in summer and very cold in winter e.g., Delhi.
Continental plate : This is a tectonic plate composed of rocks which form a large area of land as continent.
Contour : It is a line drawn on an ordnance survey map through points which are at the same height above sea level. Contour maps provide information about :
The height (altitude) of places.
The general shape of the gorund.
The steepness of sloping ground.
Contour croping : Growing of crops on strips.
Contour farming : Carrying out cultivation along lines parallel to contours.
Contour ploughing : It is a framing process of reducing soil erosion on sloping farmland.
Convection : The rising of air, water or other materials because they have been heated and are warmer than their surroundings is called convection.
Convectional rain : The rain which falls from clouds produces by convection currents is called convectional rain.
Conventional symbols : These symbols are used to represent various features on maps.
Convergent plate boundary : Another name for a destructive plate boundary. Land is destroyed where plates converge.
Core : Core is the innermost layer of the earth, with a thickness of about 3,500 km.
Corrasion : It is another name for abrasion. Any material carried by rivers, the sea, ice or the wind rubs against the ground and helps to slowly wear it away.
Corrosion : Corrosion is the solution made by certain minerals in rocks when they come into contact with water.
Cosmic rays : Radiation reaching the earth from outerspace.
Crater : Crator is a circular hole at the top of the volcano’s opening to the air or vent.
Crude oil : It is liquid petroleum.
Crust : The crust is the solid upper layer of the earth. Here molten material has cooled to form solid rock.
Cumulus : A heap cloud produced by upward buoyant convection currents.
Cyclone : Cyclone is a low air pressure area in the West Pacific, e.g. China, Japan, the Philippines, which brings severe weather similar to a hurricane.
Dairy farming : Dairy farming is concerned with the rearing of cattle for their milk.
Dawn : It is the period of diffused light before the sunrise.
DDT : A well known insecticide.
Death rate : The number of deaths per 1000 people in a year.
Deciduous forests : The forests in which trees shed their leaves for about six to eight weeks in summer.
Decomposer : Reducer is called a decomposer.
Deflation : It is the process of blowing away of small, loose materials such as sand by the wind.
Deforestation : The deliberate clearing of forest by cutting or burning large numbers of trees.
The land can be used for other purposes, e.g. farming, road building etc.
It has serious environmental effects.
Degradation : Degradation is the process of the lowering of land surface by erosion.
Delta : A delta is a low-lying area of alluvium at the mouth of a river. Deltas are formed where a river :
Carries a large load.
Enters a sea or lake with weak tides and currents.
Demography : Study of population dynamics.
Dendritic : It is the drainage pattern of river and tributeries in the shape of tree roots.
Density of population : Population density is defined as the number of people per square kilometre.
Denudation : Combined effect of erosion and weathering in wearing away the land.
Dependency Ratio : This is defined as the ratio of countrys working age population (15 to 65 years of age) and non-working age population (under 15 and over 65).
Deposition : It is laying down of sediments to make new features and landforms.
Depression : Depression is defined as the air pressure below average value in the westerly winds in temperate latitudes.
Derelicit land : Land damaged by industrial process.
Desalination : It is the removal of salt from sea water to make it suitable for use.
Desert : An area where evaporation exceeds precipitation and results in the lack of vegetation.
Desertification : It is the spread of desert into an nearby area which previously received enough rain.
Desert soils : Soils of arid regions where rainfall is less than 25 cm.
Destructive wave : These are the short, steep waves which move down a beach towards the sea about every four seconds.
Dew : It is the deposition of water on leaves of plants and ground after the water vapour in the air has cooled and condensed.
Discharge : The quantity of water flowing in a river/stream at a certain point.
Distributary : It is small river channel which comes from a larger river.
Distilled water : Water of great purity obtained by distillation process.
Distribution : It shows the features spread across an area shown up on a map.
Diurnal : Daily, applies to cycles.
Doline : A feature of karst landscape. The floors are filled with fallen rocks.
Domestic waste : Wastes from house holds including sewage and sullage water.
Dormant : A non-active volcano is known as dormant volcano.
Drainge Morphometry : The study of drainage patterns.
Drainage basin : Area of the land drained by a river system.
Drift : Slow moving mass of ocean water. The water moves in a particular direction.
Drought : A lack of rainfall over a long period causes drought.
Dry ice : Solid carbon dioxide is called dry ice.
Dry spells : These are the rainless days during the monsoon season.
Dry valley : A valley without running water.
Dune : A ridge or a hill of sand in a desert formed by the wind.
Dusk : It is the period after sunset when the light is due to diffuse.
Dust : Solid particles 1 to 100 microns in size in the atmosphere fall in the category of dust.
Dust Bowl : An agricultral region from which the soil is carried away by wind.
Dy : A type of lake bottom sediment mainly found in oligotrophic lakes.
Dyke : A narrow ridge of igneous rock formed by molten magma is called dyke.
Earth : It is one of the nine planets which has the life on it.
Earth crust : It is the outermost surface of the earth. Its thickness is 40-60 km.
Earthquake : A series of shockwaves generated on the earth crust or mantle by the shift of plates is known as the earthquake.
The point of origin of earthquake is known as focus while the point on the earth’s surface is known as epicentre.
The shockwaves are called primary and secondary waves and the surface waves are called L & R waves.
Earthquake magnitude is given on the Ritcher scale. It is the largest trace on the seismograph at a distance of 100 km from epicentre.
Ecology : The study of the relationship between living organisms and their environment is called ecology.
Ecosphere : The biosphere together with all the ecological factors which operate upon organisms is called ecosphere.
Ecosystem : Links between living things and environmental surroundings.
Emigration : It is international migration out of a country.
Energy : It is the capacity of doing work.
Epicentre : It is the point above earth’s surface directly above where earthquake starts deep in the earth’s crust.
Environment : Everything that surrounds us is called our environment.
EPA : Environmental Protection Agency.
Equator : It is defined as imaginary line of 00 latitude encircling the earth and passing half way between the north and south pole.
Equatorial climate : It is the hot, wet climate found on both sides of equator. In this climate the temperatures are high throughout the year. Rainfall is also high. In this climate rainforest is natural vegetation.
Erosion : Erosion is defined as the wearing away of the earth’s surface caused by running water, moving ice, wind and sea. It includes weathering of rocks.
Esker : A ridge of sand and gravel
Estuary : It is the lower area near the mouth of a river.
Eutrophication : Enrichment of a water body.
Evaporation : It is the process by which water from lakes, ponds, rivers and seas changes in to vapours due to the heat of the sun.
Exosphere : The outermost layer of the atmosphere above 400 km.
Extensive farming : Farming spread over a large area of land on which little capital and labour might be invested. Low yields per hectare are obtained.
Extrusive : Volanic magma/lava that reaches the earth’s surface and solidifies to form landforms.
Eye : The eye is the centre of a hurricane or tropical storm.
Fallowland : The land which is cultivated in two or three years. It is left uncultivated for sometime to regain its fertility.
Famine : It is acute shortage of food and eatables due to which people die of starvation.
Farmyard manure : Mixture of straw animal excrement used as manure in agriculture.
Fathom : Fathom is a unit of length to measure the depth of the ocean floor from the sea level.
One fathom = Approx. 6 Ft. or 1.8 metres.
Faulting : Faulting is the fracturing of rock by forces within the earth’s crust.
Fauna : Animals found on earth in the natural environment.
Fertility : Suitability of soil is for the growth of plants and crops. A fertile soil allows them to grow quickly and well.
Fertilizer : Fertilizers are used by farmers in the soil in order to gets more yields.
Flooding : Flooding occurs when :
Rivers carry more water (discharge) than they can contain within their banks.
Floods are caused by :
Heavy rainfall.
Melting snow.
Greater surface run-off due to deforestation and urbanization.
Dam or embankment failure.
The number and intensity of floods can be reduced by :
Strengthening river banks.
Deepening river channels.
Building dams.
Raising the level of a floodplain.
Diverting rivers.
Flood plain : Flood plain is the area surrounding a river, usually in its lower course.
Flora : Natural vegetation consisting of forests, grasslands and shrubs.
Fluvial : This is a general term referring to the action of rivers. and seas.
Fodder crop : Crops grown specifically in order to feed livestock. Dairy cattle farms often grow some oats and barley for this purpose.
Fog : Fog is caused by the cooling of moist air to its dew point temperature with the result that condensation of water vapour occurs.
Folding : Folding is the bending of a rock due to the of forces inside the earth’s crust.
Fold mountains : Mountains formed due to the folding of the earth’s crust e.g., Himalayas.
Forest : An extensive area of wood land, trees and animals etc. Forests are of several types such as rain forests high forests, mixed forests etc.
Fossil fuels : Fossil fuels are the remains of past vegetation which are now used as a source of energy, e.g. coal, oil and natural gas.
Fragile environment : A fragile environment is one which is particularly sensitive to the actions of people.
Fresh Water : Water with salinity less than 0.5 parts per thousand.
Freeze-thaw : When water in cracks, joints or spaces in rock freezes. On freezing it expands in its volume and exerts pressure on the surrounding rock and shatters it.
Frigid zones : The coldest zones north of the Arctic circle and south of the Antarctic circle.
Front : It is an air mass boundary. It divides air of different properties, e.g. warm from cold.
Galaxy : Cluster of stars is known as a galaxy. Our sun belongs to Milky Way Galaxy.
Genecology : The study of genetics of plants and animals in relation to their environment.
Geomorphic processes : These processes are the types of erosion and deposition which produce landforms. Landforms are the result of geomorphic processes acting upon the rocks of the earth’s surface.
Geothermal energy : This is heat and electricity produced from hot water and steam from the earth’s interior.
Glacial trough : This is another name for a U-shaped valley. These are—
Wide
Flat-floored
Steep-sided.
Glaciation : It is a long period of low temperature, heavy snow and advancing ice.
Glacier : It is a ice body which moves down a valley slowly.
Gley : Gley is a saturated soil. It developed in poorly drained conditions, often on level ground at the foot of a slope.
Globe : A replica of the earth which is true to scale.
Globalization : We live in a world in which people, places, production and the environment are becoming ever more globally interdependent.
Global warming : Rise in average world temperature during the second half of the 20th century. This warming may have either :
An artificial cause. People have been increasing the amount of certain gases, especially carbon dioxide, in the atmosphere through various activities, e.g. industrial pollution, auto exhausts. These gases may increase the natural Greenhouse Effect in the atmosphere which traps heat close to the earth.
A natural cause. Climate change, e.g. the Ice Age, has occurred throughout history. The sun, for instance, seems to have radiated more heat at one time in the past than another.
Gondwanaland : The ancient landmass situated south of the sea of Tethys.
Gorge : It is a narrow, steepsided valley cut through hard rock such as carboniferous limestone.
Gradient : It the slope of the land between any two points. It is measured from an ordance map.
Gradation : It is a natural process of lavelling of the earth’s surface.
Graphicacy : It is the drawing of maps and diagrams for geographical information, Cartographers are map makers.
Grass land : Land dominated by grass.
Graticule : The network of latitudes and longitudes on a globe used for locating places or boundaries.
Green Belt : The green belt is an green area surrounding a big town which should not be built upon. It should be preserved as open space and used only for farming and recreation.
Greenhouse effect : It is the process in the lower atmosphere in which heat radiated from the earth’s surface is prevented from escaping into space by gases and clouds.
Green revolution : A green revolution is an agricultural revolution in an LEDC (less economically developed countries). In the 1960s new kinds of wheat and rice, have been introduced into agriculture in some countries specially in India. These varieties grow at fast rate and produce high yields and more than one harvest a year. India has become almost a self-sufficient country in food because of green revolution. Irrigation, mechanization and new seeds were responsible for it.
Green manuring : Growing plants and ploughing them into the soil. It acts as manure on decomposition.
Grid Reference : A grid reference is a pair of co-ordinates on an Ordnance Survey map which allows places to be identified. Four-figure references identify a grid square with six-figure references being used to pinpoint particular places within the square. The sequence for stating a six-figure reference is :
Start in the bottom left corner of the map.
Work horizontally along the bottom of the map.
Estimate how many tenths of the way across this square the place is.
Work vertically up the left side of the map.
Groundwater : The water present underground.
Growth pole : It is the place where economic growth is concentrated.
Groyne : It is a barrier, usually wooden built at an angle to a beach in order to reduce longshore drift.
Gulf stream : It is a warm ocean current which flows to the north from the Gulf of Mexico.
Gully : It is a stream, more than half a metre deep, on a slope, often a hillside. It is formed by running water.
Habitat : The habitat is a natural home of a plant or animal or living community.
Hachures : Slopes are indicated by short lines drawn on a relief map.
Hailstone : Hard pellets and balls of ice which fall to the ground are called hailstone.
Hamra : Red sandy soil, containing clay.
Hanging valley : It is a valley which joins a U-shaped glacial trough at a level higher than the trough floor.
Hazard : Something that threatens human life and property is known as a hazard.
Headland : It is a stretch of highland coastline made of rock and projecting out into the sea.
Heat island : It is a large urban area that is warmer than the surrounding countryside.
Her bosa : Vegetation which is made up of non-woody plants.
Hibernation : Dormancy of animals like frog in winter.
High-yielding variety (HYV) : It is a variety of a crop used to produce bigger yields than the crop normally does.
Hill farming : Hill farming is used for sheep rearing on uplands and moorlands.
Hinterland : It is the area around the port with which it trades, and :
From which it draws its supplies for export.
To which imports are distributed.
Histic : Soil surface layers that are high in organic carbon.
Honeypot : It is a site to which large numbers of tourists are attracted.
Horizon : This is a distnct layer within a soil profile which can be divided into four horizons :
The H-horizon is humus and decaying vegetation.
The A-horizon is the upper layer of organic matter and minerals.
The B-horizon is the sub-soil and contains more inorganic material, especially minerals washed down from A.
The C-horizon is weathered rock fragments just above the parent material, e.g. bedrock.
Horticulture : Horticulture is related to the growing of flowers, fruit and vegetables.
Hostile environment : It is a region of the world in which natural climates are unwelcoming for people.
Humidification : Process of increasing water content of air.
Humus : It is a soil which has decomposed organic matter. It forms the top layer in most soil profiles. It is dark brown in colour. It is an important source of minerals for soil fertility.
Hurricane : A violent, revolving storm is called hurricane.
Hydraulic action : It is the mechanical loosening and sweeping away of materials by the power of moving water in a river or the sea.
Hydro-electric power : The generation of electricity by moving water is called HEP.
Hydrograph : It is a diagram which shows the changes in the discharge of a river over a period of time.
Hydrological cycle : The hydrological cycle is the water cycle. Water moves through this cycle either as a liquid or as a vapour. It takes 1000 years for water to evaporate from sea and come back to sea as rain water.
Hydrolysis : Hydrolysis is a form of chemical weathering.
Hydrosphere : Hydrosphere is the water of oceans, seas, rivers, lakes, underground water, ice-sheets and water vapour in the atmosphere.
Hygrometer : It is an instrument used for measuring the relative humidity of the air.
Ice age : This was the period when ice covered the earth surface. The most recent ice age occurred between about 3 million years and 10,000 years ago.
Ice cap : A mass of permanent ice a highland or island.
Ice sheet : It is the large mass of ice covering a big area of land.
Igneous : These are the rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molten rock (magma) from beneath the earth’s crust. Lava forms igneous rock i.e. granite and basalt.
Immigration : It is the migration of people from one country to another. It can be:
Voluntary
Forced.
Impermeable : It is a kind of rock which does not allow water to pass through because it is either :
Non-porous
Impervious
Import : Import is the purchase by residents of one country from another country of goods or services.
Improductive forest : A forest that grows slowly and has dwarf trees. It does yield products.
Infant mortality rate : It is the number of deaths of children under one-year-olds in a year for every thousand live births in that year.
Infiltration : The downward movement of water from the surface into the soil. The rate of infiltration depends upon the rainfall, water in the soil.
In-migration : In-migration is defined as the movement of people to a new area from one place to another in the same country.
Insecticide : Insect killers are called insecticides.
Insolation : The amount of heat energy radiated by the sun which the earth receives.
Instability : Instability is a condition of the atmosphere in which air continues to rise and brings a possibility of rain.
Intake : It is a part of the land on a hill farm.
Interception : Interception is defined as the process by which rain is stopped from falling directly onto the ground by trees and plants.
Interlocking spur : It is a series of ridges protruding out from alternate sides of a river valley.
Intrusive : This term is used for lava or magma which is ejected into and hardens within the rocks creating the earth’s crust.
Inversion : It is the increase of temperature with the increase of height. Normally, temperature decreases with increased altitude. Temperature inversions takes place in the early morning in valleys after a cold and cloudless winter evening.
Ionosphere : The layer of ions beyond mesophere which extends upto 400 km.
Irrigation : Irrigation is the watering of crops or plants by people rather than by rainfall. It is useful for growing crops in areas of low rainfall.
Isobar : Imaginary line drawn on the map having same pressure above sea level, which is measured in millibars (mb).
Isohaline : A line drawn on a map showing points of equal salinity.
Isohyet : It is an imaginary line on a map to join places having the same amount of rainfall.
Isotherm : An imaginary line on the map showing the places of same temperature above sea level.
Jet stream : It is a strong wind in the upper atmosphere at about 10 kilometres above the earth’s surface. Jet streams move in a wave-like pattern around the earth. The changes in the pattern of the four main jets affects the weather in the lower atmosphere.
Joint : Joint is defined as a crack in a rock by natural events. These cracks are used as lines of weakness by weathering processes for breaking the rock.
Kalbaishakhi : These winds cause rains in Bengal and Assam. They are northerly and north-westerly winds.
Key : All the symbols, abbreviations, colours and shadings used on a map are explained by a key. It is necessary for a good map.
Knickpoint : It is a break of slope for water falls in the long profile of a river bed.
Knot : One nautical mile per hour. A unit of distance for ship speed.
Lag time : It is the time-gap before river discharge responds to a change in rainfall.
Lagoon : A logoon is a region of shallow sea water along a coastline.
Land breeze : Land breeze is the wind moving from the land towards the sea at night.
Land consolidation : Knitting together of scattered farms into one unit under a common owner is called land consolidation.
Landfill : It is a fill used as dump for the ground waste.
Landform : The physical feature on the earth’s surface, like a valley is called landform.
Land reclamation : It is the turning of land which is under water into dry, useable gorund.
Land reform : Change in land ownership is called land reform.
Landslide : It is a downslope movement of soil and/or rock. Undercut by erosion at the bottom of the slope.
Lapse rate : The decrease in temperature with height in the lower atmosphere is called lapse rate. The general decrease is about 0.60C for every 100 m.
Latitude : Latitude is a location of a place on globe with respect to the Equator. Lines of latitude are drawn on maps north and south of the Equator (0 degrees) parallel with each other. The North and South Poles have latitudes of 90 degrees N and S respectively.
Lava : Lava is magma ejected from a volcanic erruption onto the earth’s surface.
Leaching : Mineral washing by flowing water down through a soil is leaching.
Levee : A levee is a naturally raised bank of alluvium at the side of a river.
Leward side : It is also called rain shadow area lies on the side away from the direction of the wind, e.g., Deccan Plateau.
Limestone : Limestone is a sedimentary rock which is permeable, soluble and contains fossils.
Literacy rate : The percentage of the adult population, who can read and write.
Lithosphere : The outer layer of the earth with the crust is called lithosphere.
Loess : The soil created from wind-blown dust.
Longitude : Longitude is the angular distance of a place on the earth’s surface from the Prime or Greenwich Meridian (0 degrees). On a map it is shown as circles joining the North and South Poles.
Long profile : This is a portion of a feature from its beginning to its end e.g., a river valley from its source to mouth.
Longshore drift : In long shore drift the beach material is moved along a coastline by the waves.
Loo : The hot dry winds which come out from the desert in summer.
Low : It is the depression in atmospheric pressure which are associated with cloud, rain and unsettled weather.
Magma : Magma is the molten rock which comes out in volcanic eruption.
Mantle : It is the second layer inside the earth below the crust. It is made of magma.
Map : A map is a diagrammatic representation of the earth’s surface on a small paper.
Marine/Maritime : These terms describe a geographical factor connected with the sea.
Marsh : Marshy ground with mineral basis is called marsh
Mass Movement : It is the movement downslope, under the effect of gravity of loose materials produced by weathering. They are of four types :
Creep : Fine and moist substances move very slowly but fairly continuously.
Flow : A mass of material which gradually slip downhill.
Slide : As a slab materials slide rapidly downhill.
Fall : Rocks come down rapidly down a slope.
Maximum-Minimum Thermometer : This thermometer records the maximum and minimum temperature over 24 hours. Six’s maximum and minimum thermometer is a U-shaped tube.
Meander : A bend in a river channel is called meander. These are a common feature of rivers all along their course.
Mechanical Weathering : Mechanical weathering is the break up of rock by the actual physical prisming apart of the separate particles.
Mediterranean : The Mediterranean Sea lies between southern Europe, north Africa and the Middle East.
Megalopolis : A megalopoils is a largely continuous built-up area of over 10 million people.
Meltwater : In glacial areas, the water coming from melting snow and ice.
Mental Map : A map that exists in the mind of a person is called mental map.
Mesosphere : A layer extending from 50 to 80 km from the earth’s surface.
Metamorphic : These are the rocks which have been changed from earlier rocks by heat and pressure. For example, marble is a metamorphic rock. Metamorphic rocks are tough and resistant to erosion, and are used for construction of buildings.
Meteoric water : Water which has fallen as rain and gone underground.
Meteoroids : Small pieces of rock and dust that burn on entering the earth’s atmosphere.
Micro-climate : Micro-climate is the climate of a very small area, e.g. a front garden.
Mid-ocean ridge : The under water mountain range rising from the ocean bed is called a mid-ocean ridge.
Mineral extraction : It is the mining of economically viable substances such as iron ore, crude oil and coal from the earth’s crust.
Mist : Mist is a light fog which cuts down visibility.
Mixed farming : This is the farming which mixes arable farming with pastoral farming.
Model : A model is a presentation of some complicated aspect of real world we live in. Models are usually shown as diagrams and focus on the relationship between a few key factors.
Monoculture : One crop growing is called monoculture.
Monsoon : Monsoon is a wind which brings rain. In summer a sea wind brings the heavy rainfall, often thought of as the monsoon (e.g. Maysinram, India with over 11,000 mm is the wettest place on the earth).
Monsoon trough : Low pressure area is called monsoon trough.
Moraine : The stoney debris left behind by the melting ice of a glacier.
Mountain : A conical mass elevated to a peak.
Mouth : The mouth is the place at which a river enters the sea.
Natural hazard : It is a threat to life and property brought by earthquakes, blizzards, drought and hurricanes etc.
Natural resource : A gift of nature such as land, forests, minerals, which is of use to people.
Natural vegetation : A natural vegetation which would grow in a place without the influence of people. In many parts of the world the natural vegetation has been changed by human activity.
Net sown area : The actual land area under cultivation is called net sown area.
Network : A network is a system of roads, railways, rivers canals in a given place.
Node : A node is a place where a transport network can be joined.
Nomadic pastoralism : It is a kind of farming in which people wander from place to place living on milk and meat from their cattle, sheep or camels.
Non-renewable : It is a natural resource which once used, cannot be replaced. It is exhaustible source e.g. coal, oil, natural gas, iron ore.
Nuclear fission : It is the breaking of nucleus of uranium by neutron bombardment and release of energy.
Nuclear power : It is the power generated by splitting the nucleus of uranium or plutonium atoms.
Occlusion : Combination of a cold front and a hot front is called occlusion.
Ocean current : It is a stream of fast flowing water which is warmer or colder.
Ocean trench : It is a long, narrow and deep trench in the ocean floor.
Offshore bar : It is a ridge of shingle slightly out to sea and not connected to the land.
Opencast mining : Extraction of minerals from the surface of the earth is called opencast mining.
Optimum population : This is the required size of population for a country.
Organic farming : This is farming without the use of (a) fertilizers (b) pesticides and (c) growth stimulants.
Orographic rain : This type of rain is caused by high relief. It is also called as relief rainfall.
Out-migration : It is the permanent migration of people from one place in a country to another place in the same country.
Overgrazing : The loss of grass and other vegetation from a grass land because too many animals, like cattle and sheep, are grazed on it.
Over population : A country having too much population for the available resources.
Ozone layer : The layer of ozone in the upper atmosphere which filters out ultraviolet light of the sun.
Ozone meter : An instrument used for measuring the amount of ozone present in the air.
Pacific : It represents the countries surrounding the Pacific Ocean.
Parallel drainage : A river system in which the streams run almost parallel to each other.
Parasitic cone : It is a cone which develops on the side of the main cone of a volcano.
Pass : A gap in a mountain range giving a natural route across for the people.
Pastoral : This is a type of farming meant for rearing of cattle and sheep, for their meat or products such as milk, wool or hide.
Pasture : The land covered with grass and used by cattle or sheep for grazing.
Peak flow : It is the maximum amount of river discharge indicated on a hydrograph.
Peninsula : It is the triangular land piece bounded by sea on three sides.
Percolation : The method by which water seeps downwards through soil and permeable rock into ground surface.
Periglacial : This is the area bordering a glaciated site.
Permafrost : It occurs when the soil and rock below the surface layer remains permanently frozen for atleast two years.
Permeable : The property of rock which allows water to pass through it. Rocks can be permeable if they are porous and pervious.
Petroleum : A naturally occuring substance made of hydrocarbons and after refining it gives many useful products.
Physical Geography : In it we study the natural environment, e.g. weather climate and soils landfroms.
Physical weathering : This is another name for mechanical weathering.
Piechart : A piechart is a circle divided into sectors or wedges. Each sector is proportional in size to the value it represents. The starting point is the North line (0 degrees). The sectors are marked in a clockwise direction in a descending order of size with the largest value first.
Plan : Plan is the drawing of very small area made using a very large scale.
Plain : A plain is a level area of grass land at low altitude.
Plantation : A plantation is a large tropical/sub-tropical farm or estate which :
practices monoculture.
it is commercial and owned by a multinational company.
produces tree or bush crops, e.g. rubber, tea.
uses a large labour force.
Plate : A tectonic plate is a large, rigid slab of the earth’s crust. The crust has large number of these gigantic slabs, up to 100 km thick, which float like rafts on the earth’s molten mantle beneath. These are oceanic plates.
Plateau : It is a level area of land higher than its surroundings.
Plucking : Plucking is the pulling of fragments off a rock surface which has become frozen to the ice. Fragments are plucked away when the glacier moves.
Plunge pool : It is the deep pool at the bottom of a waterfall.
Pollution : Pollution is the contamination of environmental factors like land, air, water etc.
Pool : Deep section of a river bed is called a pool.
Population density : Population density is the number of people living in an square kilometer.
Population distribution : It is the population spread over an area. Distributions are often studied by plotting population densities on a map. Uneven distribution of population is due to soils, vegetation, water, energy and transport.
Population explosion : A rapid growth of population is called an explosion in the world’s population that has occurred during the 20th century. Most of this explosion is now taking place in the LEDCs.
Population pyramid : It is a diagram which shows the age and sex structure of a population.
Population structure : The structure of population by age and by sex (gender).
Porous : Porous rock is one which contains a large number of small holes. Most porous rocks allow water to pass through.
Pothole : A small fairly circular hollow in the rocky bed of a river. Potholes are formed by abrasion and are common in the river’s upper course.
Prairie : These are grassland areas named after the central plain of the USA and Canada.
Precipitation : Precipitation is one which reaches the earth’s surface in the form of rain, snow fog, mist, dew and frost.
Pressure (Air) : This is the weight of a column of air on the Earth’s surface. The pressure decreases with height. Average air pressure at sea level is taken as 1000 millibars or 760 mm. It varies from place to place and from time to time at the same place.
Prevailing wind : It is the most common wind direction at a place.
Primary Meridian : The 00 longitude passing through Greenwich in England.
Profile : It has two meanings :
Soil profile : A vertical section of soil showing various horizons.
Landscape/town scape profile : A side view of a feature, e.g. a valley or a settlement.
Projection : The different latitudes and longitudes on a map useful in finding places or boundaries.
Psychrometer (Hygrometer) : This instrument is used to measure the humidity of air.
Pyramidal peak : This is a pointed mountain peak formed by glacial erosion.
Pyroclast : The solidified lava thrown out in a volcanic eruption.
Quarrying : The process of extraction of rock and minerals.
Rainfall : It is the fall of water drops from clouds onto the Earth’s surface.
There are three types of rainfall.
Relief rainfall : High relif, e.g. mountains pushing moving air upwards.
Frontal rainfall : Air rising at the fronts in a depression or cyclone.
Convectional rainfall : Warm air rising because it is lighter.
Rain guage : It is an instrument used to measure rainfall.
Raised beach : A raised beach is a platform once formed by the sea but now standing above the present sea level.
Ranching : It is the grazing of cattle or sheep on very large grass lands, i.e. ranches..
Recycling : Reuse of wastes materials.
Regional park : Area meant for recreation is called a regional park.
Relative humidity : The measure-ment of moisture in the air.
Relief : Relief indicates to the shape and altitude of the earth’s surface.
Relief rain : This rainfalls when moist air is forced to rise over an upland area. As the humid air rises, it cools, because temperature falls with height. Condensed water vapour falls as rain.
Renewable : It is a resource which on using is not diminished such as water power or wind energy, or can be grown again, like timber, or crops.
Reservoir : It is an artificial lake, used to store water which is later used in homes and industry.
Resource : A resource is anything used for production and use.
Ria : It is a flooded river valley on a coast.
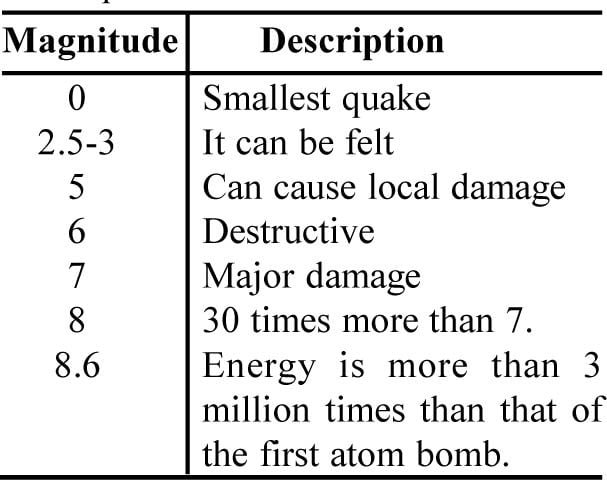
Richter scale : This scale used to measure the magnitude of earthquakes. It ranges from 0 to 10. On this scale a value of 2 can just be felt as a tremor. Damage to buildings is caused for values of over 6, and the largest shock ever recorded had a magnitude of 8.9.
Ridge : A ridge is a higher ground which is long and narrow.
Rift valley : It is a wide, flat-floored, steep-sided valley formed by stresses in the rocks around tectonic plate boundaries.
Riparian : Land bordering sea shore, lake or river.
River cliff : A river cliff is a sloping bank on the outside bend of a meander.
Rock : Rock is the solid, natural stony material forming the earth’s crust. Rocks are divided into three groups :
Igneous rocks : These include all those which have solidified from molten material.
Sedimentary rocks : These are composed of sediments either from the deposited broken material of other rocks from organic remains, or from chemical processes. Sedimentary rocks are less resistant to erosion.
Metamorphic rocks : These were originally igneous or sedimentary but have been altered by either heat or pressure within the earth’s crust.
Metamorphic rocks generally have some resistance to erosion and form uplands.
Rotation : This is the planting cycle of crops, by which the fertility of the soil is preserved. Thus, if a crop which takes lot of nutrients out of the soil, such as maize, it can be followed next year by a vegetable crop, to put nitrogen back into the soil.
Run-off : The movement of rain water over the ground and it occurs when the rainfall is very heavy.
Sand dunes : The mounds of sand deposited by wind in the deserts are called dunes.
Satellite : Small celestial body revolving around a planet. It may be natural or artificial.
Scale : Scale gives the size of the area being studied.
Scale is the relationship which exists between the map and the ground it represents. On an Ordnance Survey map it is indicated as both a statement (e.g.
1 : 50,000) and a scale line. A 50,000 scale map is 50,000 times smaller than the ground it shows.
Sea Breeze : The winds blowing from the sea towards the land during the day are called sea breeze.
Sedimentation : The process of slow setting of particles suspended in a liquid.
Seismography : It is a instrument that records the earthquake waves reaching the epicentre.
Shield volcano : It is a low, gently sloping cones resembling a shield on its side.
Shivaliks : The lowest and the southernmost mountain range of the Himalayas.
Steet : A mixture of hail and rain is called a steet.
Soil : Soil is the top layer of the earth in which plants grow.
Soil conservation : Various methods used in areas which suffer from soil erosion to conserve the topsoil.
Soil creep : Soil can creep down sloping ground because of the gravity. It is a slow process caused by wet period, followed by dry, and freezing then thawing of the ground in winter.
Soil drainage : The remoral of surplus water form the soil.
Soil erosion : Soil erosion is defined as the removal of top soil by water and wind.
1. Gullies eating into the soil. Heavy rainfall leads to gully erosion.
2. River banks crumbling, exposing soil.
3. Ploughing of the fields straight up and down hill. Rainwater flowing downhill in channel washed away the soil.
4. Continuous growing of one kind of crop makes soil more likely to be blown or washed away.
5. Overgrazing of grass lands by many animals causes erosion.
6. Cutting down trees makes protections weak for soil.
Solar : The sun is about 15 crore kilometres away from the earth. It warms the earth by radiation. This energy heats the earth and in turn the earth heats the air above it. The equator receives more sun radiation directly than any place on the earth, and this explain the higher temperatures in tropical latitudes.
Solar power : The extraction of useful energy from solar radiations is termed as solar power.
Solar system : The sun and all the celestial bodies revolving around it or family of the sun is called solar system.
Solution : Some substances dissolve in water and make solution. The dissolved substances are carried away by rivers.
Source : The starting point of a river is known as its source.
Spit : It is a ridge whose shape is like a tongue. It is of sand and/or shingle projecting into the sea but joined to the land at the other end is known as a spit.
Spring : The ground water which flows out of hill slopes and falls down.
Stars : Celestial bodies far away from the earth and which produce their own light and heat are called stars. The sun is the nearest star.
Strait : A stretch of water separating two landmasses, e.g., Palk Strait.
Stratosphere : The layer of the atmosphere extending up to 50 km from the earth is called stratosphere.
Subsistence farming : In this kind of farming farmers produce enough food for themselves and family and there is little to sell. This farming is called subsistence.
Sunrise industries : These are the new and growing industries of any time. New types of industries are of this type.
Suspension : Rivers and the sea carry in waters fine materials such as sand, silt and mud as suspended particles.
Taiga : The belt of coniferous forest found south of the Tundra in the northern hemisphere is called Taiga.
Tectonic : These are the large scale plates which shape the earth’s crust from inside. Movement of these plates produce earthquakes.
Temperate : The areas between the Tropics and the Arctic or Antarctic Circle are called temperate belts. It is in these two temperate belts that more moderate climates is found.
Temperate zones : The areas between the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle and between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle are called temperate zones.
Tethys : A long and shallow sea sandwiched between two ancient land masses is called Tethys.
Threshold population : It is the minimum population that must live in a area and its surroundings area.
Through flow : The movement of water through the soil is called through flow.
Thunder : When lightning passes through the atmosphere the air becomes intensely hot. This causes the air to expand which causes a shock wave and heard as thunder. A thunderstorm occurs at the time of heavy rain with thunder and lightning. First light is seen and then after some time thunder is heard.
Tidal : Tidal range is defined as the difference between the lowest and highest tides.
Tide : The alternate rise and fall of sea water is known as tide.
Tombolo : It is a spit which joins an offshore island to the mainland.
Topological map : This map is designed to show only a selected feature by dots, with straight lines connecting them.
Tor : The isolated mass of rock, usually granite or millstone grit, left on a hill-top after the surrounding rock has been eroded.
Torid zone : The zone lying between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn which is hottest is called torid zone.
Trade winds : These winds blow from the Tropics towards the Equator in both hemispheres. These are easterly winds.
Transitional period : The period between two seasons is called transitional period.
Tributary : A tributary is a channel of a river which flows into another, usually larger one.
Tropic : One of two lines of latitude 23½ 0 away from the equator; the Tropic of Capricorn lying to the south of the equator and the Tropic of Cancer to the north.
Tropical rainforest : These are the dense, tall forest found always in hot, wet climates in parts of the Tropics.
Troposphere : The atmospheric layer closest to the surface of the earth is called troposphere.
Tundra : Tundra is on the edge of polar ice caps, the area of northern Canada and northern Russia. On these barren lands only hardy shrubs, mosses and lichens grow.
Universe : Everything that exists in included in universe. It contains solar system, stars, planets, galaxies etc.
U-shaped valley : A U-shaped valley is another name for a glacial trough.
Valley : It is an area of lowland, usually broader at its head than at its mouth, cut by a river. Glaciers can modify a river-cut valley.
Velocity : The distance travelled a the river water per second or per hour.
Vent : The opening through which a volcano ejects material.
Volcano : The opening of the earth’s crust out of which lava, ash, and gases erupt is known as a volcano. Most volcanoes lie at plate boundaries. A big noise is produced.
V-shaped valley : This type of valley is an unglaciated river valley whose cross-section resembles an open V in shape.
Water divide : A raised landform which divides two or more drainage basins.
Water cycle : Time taken by water to go from one place and come back to the same place. It is about 1000 years.
Waterfall : A sudden vertical fall of water in the course of a river from a height is called waterfall.
Waterlogging : Saturation with water is called waterlogging. It takes place after heavy rain, especially in clay soils or when the soil has a layer of impermeable rock underneath it.
Water table : The underground water level in the rocks, below which the rocks are permanently saturated is called water table.
Water vapour : Water vapour is defined as water in gaseous form.
Wave : High rising water which continuously amends the coastline is known as a wave.
Wave-cut Platform : A wave-cut platform is a fairly level area of solid rock on a coastline.
Weather : For a short period, weather refers to the atmospheric conditions at any location.
Weathering : It is the breakdown of rocks through exposure to the atmosphere. Rain, wind, heat, frost, temperature change and organisms.
Weather map : A map on which meteorogical variables are plotted for large geographical region for a particular time.
Westerlies : Westerlies are the winds blowing from the west.
Wet spells : Wet spells are the monsoon rains at a stretch.
Wind belt : The zone of the earth, where prevailing winds, like the westerlies or the trade winds, predominate.
Wind energy : The energy of the wind used by windmills is called wind energy.
Wind erosion : It is the removal of rocky material by the wind.
Wind gap : A wind gap is a pass through an upland or ridge which is not occupied by a river.
Wind vane : Wind vane is a pivoting needle used to show the wind direction.
